Explain the Difference Between a Dipeptide Polypeptide and a Protein
A peptide is two or more amino acids joined together by peptide bonds. Building blocks that make up proteins.
The fundamental difference between polypeptide and protein is that the polypeptide is formed from Sagar amino acids coming together through peptide bonds whereas a protein structure is made when many polypeptide chains come together.
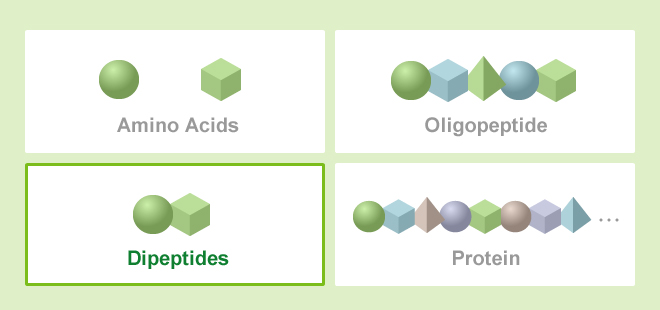
. A polypeptide is more that two amino acids linking together. As nouns the difference between polypeptide and peptide is that polypeptide is organic chemistry any polymer of same or different amino acids joined via peptide bonds while peptide is biochemistry a class of organic compounds consisting of various numbers of amino acids in which the amine of one is reacted with the carboxylic acid of the next to form an amide bond. When a polypeptide contains more than 50 amino acids then it is known as protein.
Some proteins function as enzymes some as antibodies while others provide structural supportAlthough there are hundreds of amino acids found in nature. Difference between polypeptide and protein. In addition peptides tend to be less well defined in structure than proteins which can adopt complex conformations known as secondary tertiary and quaternary structures.
Peptides are short amino acid chains. Proteins have complex shapes that include various folds loops and curves. Amino acids bind with each other through peptide.
There are two general classes of protein molecules. Although peptides and proteins are the same as both are made up of amino acids but the peptide chains are shorter than proteins. When two amino acids join the result is called a dipeptide three gives a tripeptide etc.
A dipeptide is a protein that contains two amino acids. Two amino acids constitute a dipeptide while three or more create a polypeptide. These will be methionine.
Peptides are smaller than proteins. Traditionally peptides are defined as molecules that consist of between 2 and 50 amino acids whereas proteins are made up of 50 or more amino acids. Proteins have hydrogen bonds disulfide bonds and other electrostatic interactions which governs its three dimensional structure in contrast to polypeptides.
A chain consisting of three is a tripeptide. Peptides are short polymer linked by peptide bonds. Therefore proteins are long chains of amino acids held together by peptide bonds.
Peptides can be dipeptide tripeptide and polypeptide depending upon the relative position of the amino group with respect to the carboxyl group. Describe the differences between the primary secondary tertiary and quaternary levels of protein structure. If there are more than fifty amino acids this is now considered a protein.
Chemical bonding between portions of the polypeptide chain aid in holding the protein together and giving it its shape. Folding in proteins happens spontaneously. By convention peptide and protein structures are depicted with the amino acid whose amino group is free the N-terminal end on the left and the amino acid with a free carboxyl group the C-terminal end to the right.
Peptides are short chains of amino acids. A chain consisting of only two amino acid units is called a dipeptide. The key difference between oligopeptide and polypeptide is that oligopeptides contain few amino acid residues whereas polypeptides contain a large number of amino acid residues.
Describe how a peptide bond is formed between two amino acids to form a dipeptide. Define dipeptide tripeptide and oligopeptide and polypeptide. The secondary structure of a polypeptide is.
A polypeptide is a chain of many amino acids. Proteins are produced from two or more polypeptide chains. As nouns the difference between dipeptide and polypeptide is that dipeptide is biochemistryorganic chemistry an organic compound formed from two amino acids joined by a peptide bond while polypeptide is organic chemistry any polymer of same or different amino acids joined via peptide bonds.
In summary here are the differences between a peptide bond and a polypeptide. Proteins have a higher molecular weight than polypeptides. Multiple amino acids result.
The terms oligopeptides and polypeptides come under the category of proteins. Short protein of two amino acids held together by a peptide bond. The union of two or more polypeptides quaternary structure.
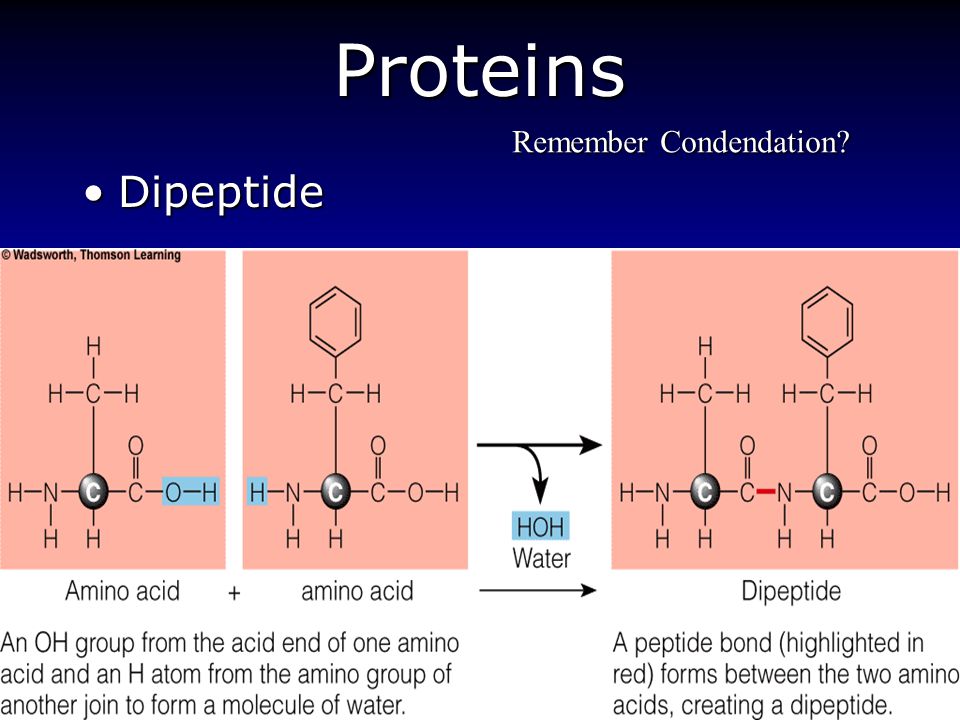
2 marks condensation reaction between amine and carboxyl group. All peptides have an N terminal and C. Secondary structure is when the polypeptide chain coils or folds into a specific pattern alpha helix - coiled polypeptide chain beta pleated sheet - folded polypeptide.
This bond is formed between the alpha amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of another in a condensation reaction. One or more polypeptide chains twisted into a 3-D shape form a protein. Polypeptides have a molecular weight that is much lower than that of proteins.
The main difference between polypeptides and proteins is that polypeptides have lower molecular weight than proteins. The milk contains a high concentration of protein. Both polypeptides and proteins can be found in biological systems.
And a protein contains one or more polypeptides. Explain the role of these cell adaptations in the production and secretion of breast milk. Polypeptides are continuous and longer peptide bonds with more than fifty monomer units.
Polypeptides that have fewer amino acids are known as proteins. Polypeptides are long amino acid chains. Special chemical bonds that hold amino acids together.
A dipeptide consists of two amino acids linking together. Amino acids are organic molecules that when linked together with other amino acids form a proteinAmino acids are essential to life because the proteins they form are involved in virtually all cell functions. Polypeptides are amino acid sequence whereas proteins are made by one or more polypeptide chains.
Primary structure is a proteins unique sequence of amino acids. Peptides are short polypeptides are long. Peptide just refers to two or more amino acids liking together.

Dipeptide An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Difference Between Peptide And Dipeptide Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms

Peptide Bond Definition Formation Degradation Examples Peptide Bond Peptides Bond

Learn About Dipeptide Chegg Com

Reflection Vii Amino Acids Proteins P2 Macromolecules Protein Amino Acids

Amino Acids Part 5 Of 5 Peptides Polypeptides And Peptide Bonds Youtube

Difference Between Peptide And Dipeptide Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms

Chapter 2 Chemistry Of Cell Proteins Peptide Bond Biochemistry Amino Acids
No comments for "Explain the Difference Between a Dipeptide Polypeptide and a Protein"
Post a Comment